Plant-Based Proteins: The Nutritional Powerhouse for Health
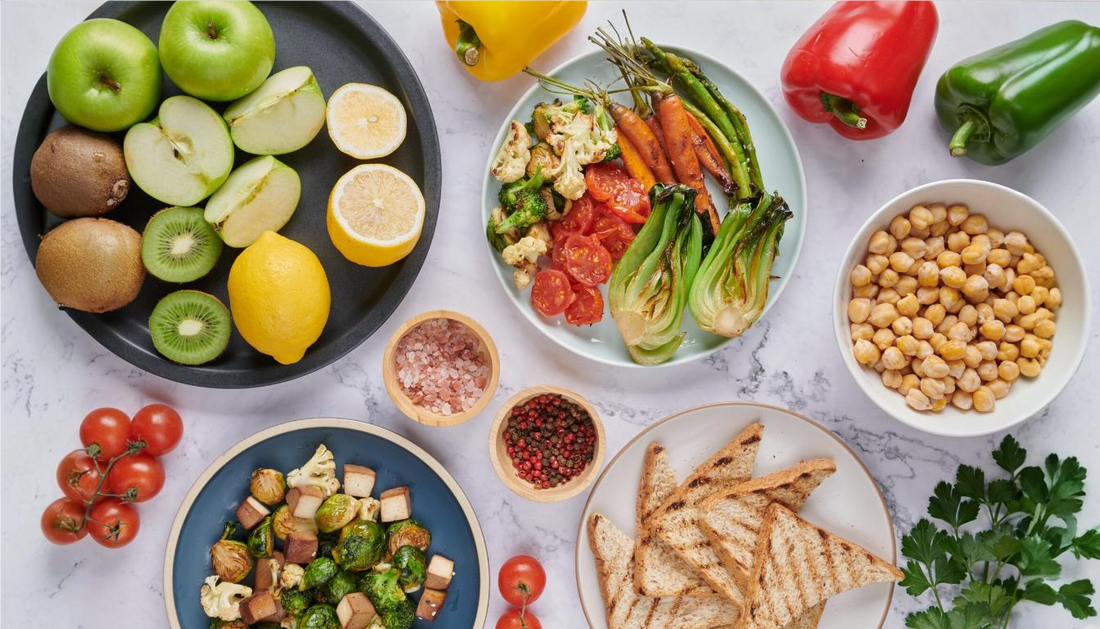

Protein has become particularly trendy as consumers increasingly seek higher levels of plant and animal-based products to complement their diet. Even though not all protein intake contributes equally to the same purpose, more application of plant-based proteins can enable a person to fulfill their dietary requirements with minimal eco-friendly benefits. Today, there are various forms of plant-based options, such as soy, pulses, nuts, and spirulina, that are delivering savory and high protein meals for people aiming to reduce their intake of animal-based products.
How can plant-based proteins improve health?
Plant-based proteins have the potential significantly to improve health through nutritionally and sustainable substitutes for products based on animals. Being rich in essential nutrients, including vitamins, minerals, and fiber, plant-based proteins support overall wellness and hence, it can enhance immunity.
1. Being relatively saturated with fewer fats, plant-based proteins are less likely to cause heart disease, one of the fast-growing diseases in the country.
2. Addition to these, plant-based foodstuffs like lentils, beans, and tofu reduce obesity and maintain healthy body composition for consumers.
3. Most of these foods are estimated to have reduced chronic ailments including diabetes and specific cancers.
As healthier lifestyles become the new filicide for Indians, plant-based proteins make a perfect fit for both human health and environmental health.
These are the important benefits of plant-based proteins for our bodies:
- Deliver essential nutrients, vitamins, and fiber.
- Control weight by consuming fewer calories.
- Lower saturated fats and therefore fewer chances at heart disease.
- Low risk of serious, long-term diseases like cancer and diabetes.
- High Amount of Fiber Promotes Your Digestive System.
- Less damage to the environment and less resource-intensive to produce.
- Flexible and best suited to almost all types of nutritional foods.
Growing Popularity of Plant-Based Diets: A Shift Towards Healthier Living
More people realize the importance of this diet, mainly in terms of health and a greener environment to reduce dependency on animal products. Plant-based diets are, therefore, gathering momentum in India.
1. Traditionally, Indian diet has been high in plant-based foods, including legumes, beans, vegetables, and grains, and the change-over is easier and culturally in line.
2. In keeping with such an emphasis on heart disease, diabetes, and obesity, eating plant-based can simply become a holistic route to becoming healthier, losing weight, or reducing the risks of chronic diseases.
3. Increasingly also, with a growing consciousness of environmental risks, eating plant-based food becomes more environmentally responsible, with less carbon footprint than a diet based on meat.
4. Yet another reason the trend is picking up is the increase in availability of plant-based substitutes, be it milk substitute or even meat.
5. The awareness and demand for plant-based foods are also increasing in urban areas as restaurants, food brands, and influencers are increasingly talking up this lifestyle.
The more places become available, the more people are supposed to start adopting a plant-based diet across India.
What are the Key Sources of Plant-Based Protein?
Important sources of plant-based protein in India are listed below:
1. Whole Grains: Quinoa, millet, and brown rice are good sources of protein, fiber, and some needed micronutrients. These help keep our gut in great condition, promote weight, and impart sustained energy.
2. Lentils and Legumes: These are protein, fiber-rich foods with essentials minerals-rich legumes that are inexpensive, the staple of most Indian dishes. They regulate blood sugar levels, and the quality of them help the heart be healthy too.
3. Nuts and Seeds: The nuts and seeds are made of much more quantity of healthy fats, fibers, and proteins. So, the brains go well health wise with nuts, enhance the energy levels, and offer a balanced diet. They reduce the cholesterol level present in human body.
4. Peas: Green peas are a good source of protein, vitamins, fiber, and antioxidants. These support muscle recovery and also maintain proper digestive health.
5. Tofu and Tempeh: These soy-based products constitute high amounts of proteins, thus giving one a great alternative for vegetarians and vegans; further, they are rich sources of all nine essential amino acids, hence completing the protein food.
6. Vegetables: They are not high in protein, contain essential proteins along with other vital nutrients such as vitamins, minerals, and fibers, helping overall body well-being.
7. Leafy Greens: Although they contain a minuscule amount of proteins, leafy greens like spinach and kale are richly contained in vitamins, minerals, as well as antioxidants that build quite an important contribution to health and immune support.
8. Plant-Based Dairy: The alternative products, such as almond and soy milk, contain proteins but saturated fat levels are not comparable to the former. For a vegan diet or for a lactose intolerant individual, these can be used.
Research [1][2][3] into the effects of consumption of plant proteins in reducing the risks of cancers found that one of these benefits is the reduction in incidence of colorectal cancer. Some research also showed people with certain genetic mutations linked to fat metabolism are at risk to develop colorectal cancer if their diet is composed mainly of meat. In this case, replacing animal-based protein with a plant-based protein source could result in the reduced incidence of developing colorectal cancer.
What are the health benefits of plant-based proteins?
- Low prevalence of chronic diseases: conditions such as diabetes, hypertension, and some cancers
- Heart health: low saturated fats with healthy levels of cholesterol and with heart diseases
- Weight control: high content of fiber encourages fullness and weight loss.
- Rich sources of antioxidants: averts inflammation and oxidative stress.
- Enhances digestion: it is also high in fiber; hence it encourages digestive health and resistance to constipation.
- Helps regulate blood sugar: Blood Sugar is stabilized and useful for people suffering from type 2 diabetes.
- Production of plant-based proteins is developed with a much lesser environmental footprint than that of proteins in animals.
What are the environmental impacts and health benefits of plant-based proteins?
Plant-based proteins produce significantly less environmental impact than do animal-based proteins.
1. Sources of plant-based proteins require much less water, land, energy, and contribute much less to greenhouse gas emissions, thus gaining a heavy edge for the earth.
2. Plant-based proteins, thereby, incorporated into diets, can reduce deforestation, conserve fresh water resources, and mitigate climatic changes.
3. These benefits are thus tremendously given by the dietary protein from plant sources, considering health from which its several advantages include improving heart health, weight management, and easy digestion because of the high fiber content.
4. It would further decline instances of diseases such as diabetes, hypertension, and many more cancers.
5. Plant-based proteins are also rich in nutrients and antioxidants that help maintain general health and nurtures immune health.
Region may vary with common allergens, as is evidenced by sesame seeds in Canada, mustard in the EU, and buckwheat in Japan, and as plant protein consumption continues to rise, the likelihood of allergic responses may also be due to widespread early-stage consumption of these foods.
Conclusion:
In short, plant-based proteins are both nutrient-dense and a sustainable way towards healthy outcomes for Indians. More prevalent sources of plant-based proteins- including lentils and legumes, nuts, and seeds - translate into enhanced heart health, bodyweight management, reduced risks of chronic diseases, and an even greener, more sustainable for each one. Change to plant-based proteins for better personal and the planet's health. Eat healthy food and turn earth as a healthy place by trying out all plant-based options.
FAQ’s:
1.How do I know that I am getting enough protein on a plant-based diet?
Ensuring proper intake of protein while on a vegetarian diet entails having a number of proteins like lentils, beans, quinoa and nuts in the diet. The intake of various plant sources throughout a day will allow you to achieve the protein requirement in a day.
2.What are the best sources of complete proteins?
There are only three complete protein sources on a plant-based diet- quinoa, soy and hemp- which contain all the important amino acids essential for body health at its best.
3.Are plant-based protein powders effective?
Plant-based protein powders, such as pea, brown rice, or hemp varieties may prove useful for supplementing your diet if you are unable to get enough from food alone.
No comments























0 comments